![flor-silvestre_borboleta[1]](https://montalvodotblog.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/flor-silvestre_borboleta1.jpg?w=661&h=441)

PHRASAL VERBS.
It is a compound verb formed by the combination of a verb and a grammatical particle, ie an adverb or a preposition, or even by a verb followed by an adverb and a preposition. Like many other verbs phrasal verbs often have more than one meaning.
Verb + adjective.
Verb + preposition.
Verb + adverb.
A phrasal verb is a compound verb that contains a verb and a prepositional adverb or particle. Together, these form a semantic unit. A phrasal verb may also appear as an idiom.
Phrasal verbs can be both transitive and intransitive, separable and inseparable, which is why they are often referred to as “two-part verbs.” The English language contains a number of phrasal verbs, such as “tear off,” “pull through,” and “run out.” Almost all of these phrasal verbs have multiple meanings. In the sentence “Put out the light, and then put out the light.” (Othello, by William Shakespeare), Shakespeare has used the phrasal verb “put out” twice.

Separable: They are those phrasal verbs in which one can put a person of the predicate, in the middle of the action and the preposition.
Example: -take back
Max took the defective radio back to the store where he bought it.
Inseparable: Are those phrasal verbs in which the verb and the preposition always go together and do not separate, that is, the object pronoun is always put after the preposition.
Example: -come along
Things are coming along well.
Transitive: have a direct object.
Intransitive: do not have a direct object.
Some phrasal verbs can be both transitive and intransitive, as we can see here with the verb look up:
– look up (‘get better, improve’) = intransitive:
After a horrible year last year things are starting to look up.
The verb look up with the above meaning is intransitive, so it has no object.
When look up means ‘look for a word’ it is transitive – words is its object:
– look up (‘look in the dictionary for a word’) = transitive:
I often look up words in the dictionary.
EXAMPLES:

Clause = Phrase. In grammar a clause or phrase is merely a group of words which typically includes a noun and a verbs, but whose meaning is not compute or defined.
Sentences differ from clauses because the meaning of sentences is always full. Clauses, by the other hand, would be awkward or incomplete if they were alone.
An adjective is any member of a class of words that modify nouns, noun phrases and pronouns, primarily by describing a particular quality of the word they are modifying.
RELATIVE CLAUSES.
Are sentences which add information about a noun.
A relative clause is a clause that usually modifies a noun or noun phrase and is introduced by a relative pronoun (which, that, who, whom, whose), a relative adverb (where, when, why), or a zero relative. Also known as an adjective clause, anadjectival clause, and a relative construction.

Relative pronouns:
Who —> Paople.
Which —> Things Animal.
That —> People / Things Animal.
Where —> Places.
When —> Time.
Subject and object relative clauses.
I am taking cooking lessons.
The teacher WHO gives the classes appears on tv.
Subject: WHO.
The are the cookies WHICH we prepared today.
Object: WHICH.
EXAMPLES:

VOCABULARY.
Grew up: Increase in size, quantity or intensity a thing.
Going out: Going from a closed or limited place to the outside, through an opening or passage.
Work out: A routine is a habit or habit that is acquired by repeating the same task or activity many times. Routine involves a practice that, over time, develops almost automatically, without the need to involve reasoning.
Break up: Make a body or a substance, when mixed with a liquid, undo until its particles are incorporated into said liquid.
Moved away: Going to live in another house or place different from where it was established.
Went away: Move from one place to another.
Put them away: Place something in an appropriate place.
Hook it up: Joining or establishing contact between two parts of a mechanical or electrical system.
Turn it down: Deny a request or instance.
Reject an offer or application made by someone.
Turn it up: It’s usually said when someone doubts someone else’s sincerity, veracity or actions.
eg. If I said to you, I was late cos of an accident on the road. And you didn’t believe me. You could respond ‘Come on, turn it up!». (eg. gimme a break, tell the truth).
An animated film: «Cinematic animation» is the recording of phases of an imaginary action created individually, in such a way as to produce illusion of movement when projected at a constant and predetermined rate, higher than that of the persistence of vision in the person.
A horror movie: The most important feature of the horror genre is the effect that is caused on the audience, the horror must necessarily provoke fear in the or the viewer.
A (romantic) comedy: The basic plot of a romantic comedy is that two people know each other, joking among each other, but despite the obvious attraction to the audience, they are not romantically involved by some kind of internal factor (outwardly they do not like each other).
A science-fiction movie: It uses speculative representations based on the science of imaginary phenomena such as extraterrestrials, alien planets and time travel, often along with technological elements such as futuristic spaceships, robots and other technologies.
A thriller: An advance, trailer (anglicism trailer) is synopsis is a piece of video or similar that presents a summary of a film, a television series, a music video.
CONDITIONALS.
All kinds of conditionals are formed of two clauses:
The IF clause marks the condition.
The RESULT clause mariss the consequences.
According to the situation we want to express we can use 1 of 4 different kinds of conditionals.
In these sentences, the preposition «if» adopts the «past perfect» and the main clause the «present conditional». You would have picked it up and put it outside.
Conditional sentence type 1.
→ It is possible and also very likely that the condition will be fulfilled.
Form: if + Simple Present, will- future.
Example: If I find her address, I’ll send her an invitation.
Conditional Sentence Type 2.
→ It is possible but very unlikely, that the condition will be fulfilled.
Form: if + Simple Past, Conditional I = (would + Infinitive).
Example: If I found her address, I would send her an invitation.
Conditional Sentence Type 3.
→ It is impossible that the condition will be fulfilled because it refers to the past.
Form: if + Past Perfect, Conditional II = (would + have + Past Participle).
Example: If I had found her address, I would have sent her an invitation.
EXAMPLES:

QUESTIONS.
Yes/No:
The only posieble answered.
They staet with an ausiliary verb.
Interrogative Word/Phrase + Auxiliary + Subject + Action Verb + Complement + ?
Information:
They are answered with specific information.
They start with an interrogative word/phrase.
Indirect questions.
In circumstances where the same meaning can be expressed by an indirect question depending on a verb of speech, or by a relative clause modifying an (implicit or explicit) object of that verb, which is more idiomatic in Classical Latin?
Example: «He related to me what had happened.» This can be cast as an indirect question.
SEPARABLE PHRASAL VERBS WITH OBJECTS.
How do yo:
Turn on the game controller?
Turn the game controller on?
Turn it on? (Not turn ot it).
Question word + to + verb.
Let me show you what to do.
Can you show me how to turn it on?
Do you know where to plug it in?

PRESENT PERFECT AND PRESENT PERFECT CONTINOUS.
Present perfect is used with completed actions.
Present perfect focuses on the end result of the action.
Present perfect continuous is formed by adding «has been» or «have been» to the present participle.
Present perfect cannot be used for temporary actions.
Present perfect indicates how much/many have been completed.
Present perfect continous is used with ongoing actions.
Present perfect continous focuses on the action itself.
Present perfect is formed by adding «has» or «have» to the past participle.
Present perfect continous can be used for temporary actions.
Present perfect continuous indicates how long something has been happening.

STATIVE VERBS.
Stative verbs are verbs that express a state rather than an action. They usually relate to thoughts, emotions, relationships, senses, states of being and me asurements. These verbs are not usually used with ing in progressive (continuous) tenses even though they may take on time expressions such as now and at the moment. We use the simple tenses for them.

Express a permanent state rather than an action and are not used in the continuous form.
These are:
– Verbs of the senses.
– Verbs of feelings and emotions.
– Verbs of opinion.
– Other verbs.

EXAMPLES:

PARTICIPLE ADVERBS.
An adverbial participle formed using an imperfective verb denotes a process, an incomplete action.
An adverb is a modifying part of speech. It describes verbs, other adverbs, adjectives, and phrases. They are used to describe how, where, when, how often and why something happens.
Adverbs describe:
How: Slowly, carefully.
When: Always, sometimes, yesterday.
Where: Here, there.

EXAMPLES:

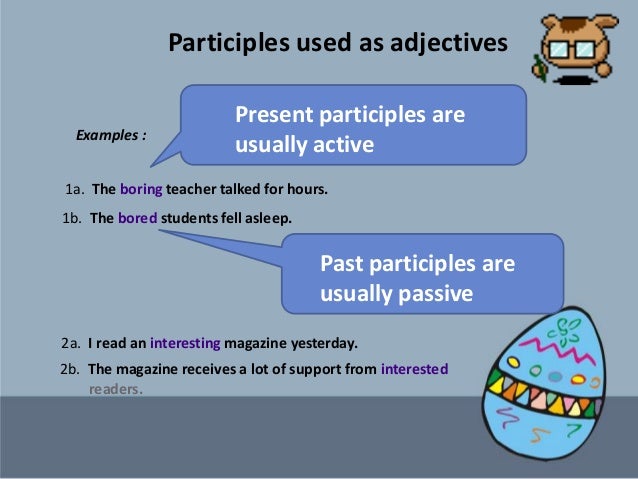
PARTICIPLE ADJECTIVES.
Some participles (like ‘bored’ or ‘boring’) can be used as adjectives. These are used in a slightly different way from normal adjectives. We usually use the past participle (ending in -ed) to talk about how someone feels:
- I was really bored during the flight (NOT: I was really boring during the flight).
- She’s interested in history (NOT: She’s really interesting in history).
- John’s frightened of spiders (NOT: John’s frightening of spiders).
We usually use the present participle (ending in -ing) to talk about the person, thing, or situation which has caused the feeling:
- It was such a long, boring flight (so I was bored).
- I read a really interesting book about history (so I was interested).
- Many people find spiders frightening (so they’re frightened when they see spiders).
We usually use the past participle (- ed) to talk about some one’s feelings and the present participle (- ing) to talk about cause of the feeling.

EXAMPLES:
List.
Past Participle (- ed). Present Participle (- ing).
Alarmed. Alarming.
Aggravated. Aggravating.
Amazed. Amazing.
Annoyed Annoying.
Bewildered. Bewildering.
Caprivited. Capriviting.
Challenged. Challenging.
Disgusted. Disgusting.
Distressed. Distressing.
Disturbed. Disturbing.
Enchanted. Enchanting.
Encouraged. Encouraging.
Energise. Energising.
PARTICIPLE ADVERBS AND PARTICIPLE ADJECTIVES.
Difference:

Adjective Adverb
I drove that very car. It is very hot.
The cat is not well. She performed well.
She is a fast reader. Don’t go so fast.
It was a straight shot. I can’t shoot straight.
It was a just decition. She just arrived.
We had a late lunch. It happened late in the day.
You have set a low bar. Don’t sink so low.
I have high standards. I can’t jump very high.
That test was hard. Don’t push so hard.
VOCABULARY.
Bored. It implies or denotes boredom.
Fascinated. Fascination is a state of mind and soul of a person who makes the individual appear fully and entirely interested, attracted or fanatized by a phenomenon (for example, by football) or by a person.
Interested. That has interest in one thing
Embarrassed.We usually use the term baffled when we want to realize that we have been extremely surprised, stunned or hallucinated by the succession of a certain fact that was not expected to happen or by an extraordinary situation, surprising and even spectacular that dislodges the recipient or viewer.
Pleased. He is satisfied with good behavior or good work.
Frustrated. He has a feeling of frustration or has had it at some point in his life and has been marked by him
Disappointed. Disappointment is a feeling of dissatisfaction that arises when expectations about a desire or a person are not met. It is formed in uniting two primary emotions, surprise and grief. Disappointment, if it lasts, is a trigger for frustration and later, depression.
Scared. That shows or denotes fright.
Surprised. Surprise is a brief emotional state, the result of an unexpected event.
Excited. It is the passive participle of the concept emotion and is very frequent in the daily discourse.
Jealous. You feel jealous of something or someone.
Anxious. Who feels craving (craving).
Worried. You worry or tend to worry about some stressful situation.
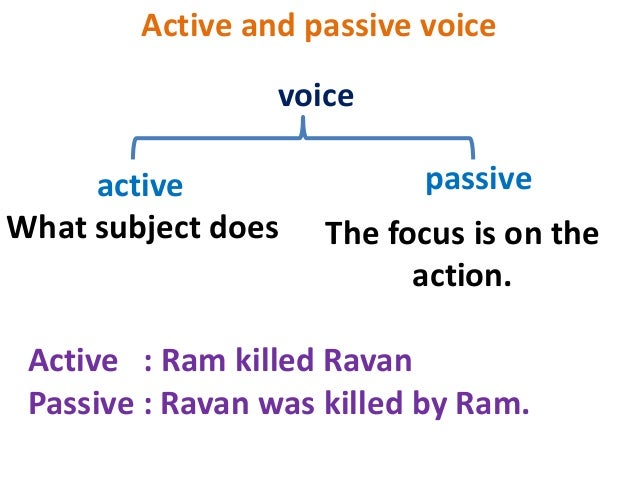
PASSIVE VOICE.
In active voice, the subject performs the action.
Example: John hit the ball.
In passive voice, the action is performed on the subject. The subject receives the action.
Example: The ball was hit over the fence.
Use of passive.
Passive voice is used when the focus is on the action. It is not important or not know, however, who or what is performing the action.
Form of passive.
Is passive voice object plos verb to be.
The voice is traction to voice pass action verb in pass participle pass complement.
For sentences in the active voice, the subject performs the action; for those in the passive voice, the subject receives the action. Most grammarians recommend using the active voice whenever possible.
Two elements esencial ver to be and verb past participle.
Subject verb object.
Past is voice and any tenses and by we modal verbs.


EXAMPLES:
Active voice:
– The man caught several fish.
– The planning committee discovered that the room wasn’t available.
Passive voice:
– Several fish were caught by the man.
– It was discovered by the planning committee that the room wasn’t available.
VOCABULARY.
Hit. Give one or more blows to a person, animal or thing using his body, a part of him or an object.
Damaged. That is broken.
Heavy. Which weighs a lot or has more weight than is normal. Which is difficult or expensive to perform because it requires a lot of effort or a lot of attention.
Strong. It resists continuous use, friction or is firmly attached and is difficult to pull off, remove or break.
Severe. That it has or can have danger or detrimental consequences.
Thunder. Very loud noise that follows the lightning during a storm, produced by the expansion of the air to the passage of the electric discharge.
Lightning. Live and momentary glow produced by a clash of stormy clouds charged with static electricity.
Destroyed. Destroy refers to damaging or rendering unusable a material object, it could be an action that is done consciously and with the intention of ruining this property, or it could also give the situation of doing it by accident.
Tornado. Gigantic air funnel, which spins cyclonic upward spiraling, whirling, produced by the interaction of a violent storm with winds in the troposphere; Originates in the Gulf of Guinea and in Central and North America.
Hail Storm. Hail storms are localized events that typically occur in the spring or fall. Although usually these storms do not cause much damage, when the hail reaches a size of 1.5 inches can cause a lot of damage to cars, glass and external walls.
REFLECTION.
English is very important because it is useful in many things, you must learn to speak it and practice it so that over time you will have experience and learn to speak it and pronounce it correctly. For any job in which people perform is of paramount importance, as it is the most widely used language anywhere in the world.
In the career that I am studying which is a Degree in Psychology I am going to use it to read articles or if at any moment I want to go to work in another country or place that does not belong to Mexico I will have to know to speak English, Way to communicate with other people; Besides that psychology consists mostly of having contact and communication with patients or clients and all the time I have to speak either in Spanish or English depending on where I am and the person I am attending.
So you must learn to speak English so you can communicate with people and be able to have a better salary in any job where you want to establish and in the country where you want to be living, regardless of the career being studied or carried out.























